HashMap的源码查看
HashMap是常见的,以K-V存储的数据结构.
在看源码之前,先需要了解HashMap的结构情况,前面的代码中也可以看到主体数据是由Node<K,V>组成的数组构成,而Node还有指向下一节点的指针,参考下图:
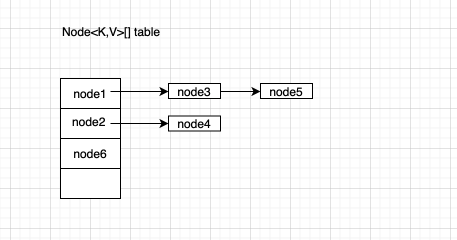
Node节点
首先看到hashmap中的node类继承了map.Entry<k,v>结构,有类型为K的key和类型为V的value;其次node是一个单链表结构。
1 | static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { |
HashMap源码
基本属性
1 | /* 实际上结构就是一个类型为Node的数组,使用transient 防止对整个table全部序列化 */ |
hashMap的三个构造方法
1 | /* 第一个参数 是默认的初始化阈值大小,第二个是加载因子大小 */ |
hashMap的方法源码
在大致了解完HashMap的结构后,通过查看put方法,来分析元素是如何放到这种结构中的。大致步骤可以参考下图:
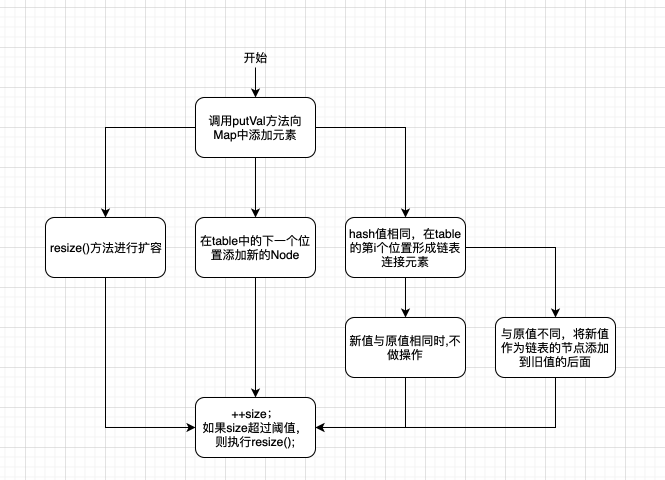
put方法
1 | public V put(K key, V value) { |
在看get方法之前先看和put方法息息相关的resize方法
如果 hash&length-1 的值重复的话,说明位置冲突,首先会添加在这个位置元素后面,如果大小超过 TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1 的时候自动为这列整理成树形状。这样就会变为数组和横向列表或树的组合结构。
在未重复hash的前提下,如果table的大小超过设置的 threshold 的大小的时候,就会触发 resize 方法。在resize时会将HashMap中的所有元素进行重新排列,以便与防治分布不均匀的情况发生。下面就来看看resize方法的代码结构。
1 | final Node<K,V>[] resize() { |
get方法
get方法是根据hash和key值进行查找,同理containKey方法也是调用getNode方法进行判断。
1 | public V get(Object key) { |
remove方法
使用remove方法根据key移除节点
1 | public V remove(Object key) { |
keySet方法
ketSet方法也是经常用到的方法,keySet方法实际上就是返回新建的keyset结构。具体结构可以看如下代码,可以看到只有使用forEach和Iterator方法的时候才会循环tab来找key的set数据。数据结构中都是调用外部方法的方法。
1 | final class KeySet extends AbstractSet<K> { |
这是几个非常常用的hashMap的方法和基本的数据结构源码的分析查看。就当做笔记记录一下。