LinkedList的源码查看
结构源码
LinkedList是一个双向链表,因为它具有next和prev的前后引用。所以每次添加元素,移除元素时,需要考虑两个指针的引用情况,保证对前一个元素的完全断开和新元素的完全引用,如果在指定位置上连接元素的过程和结构可以参考下图:
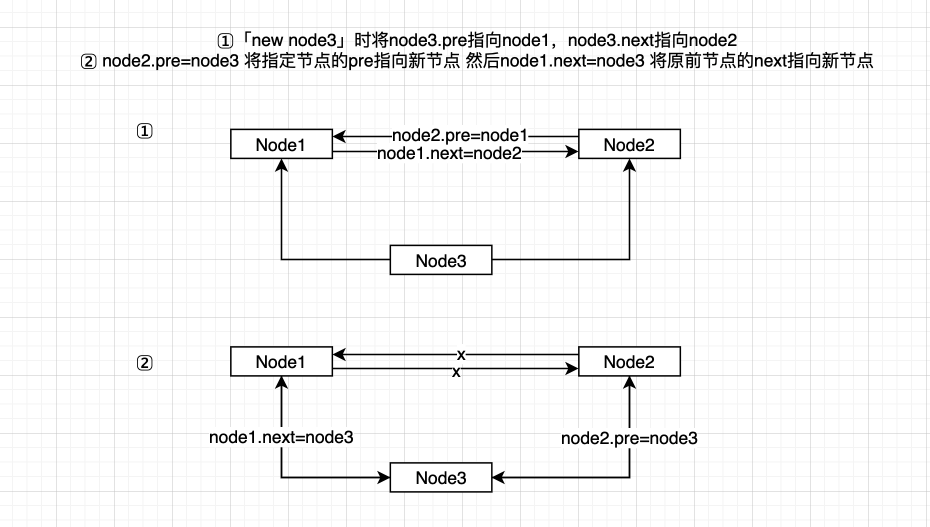
依赖结构
1 | /* LinkedList的内部变量 可以看出LinkedList其实就是一个链表 */ |
LinkedList构造函数
1 | /* 空构造函数 比较常用 */ |
基本方法
添加
1 | /* add方法默认调用linklast方法,也就是向后添加元素 */ |
使用add方法后会默认的调用 linkLast 后将元素添加至List的末尾。
1 | void linkLast(E e) { |
当然也可以调用方法在最前面添加元素
1 | public void addFirst(E e) { |
移除
remove方法
1 | public E remove(int index) { |
removeFirst
1 | public E removeFirst() { |
removeLast 和removeFirst同理
赋值取值操作
get方法
1 | public E get(int index) { |
set方法
1 | public E set(int index, E element) { |
LinkedList中的栈操作
peek方法
1 | /** |
同理 peekFirst 和 peekLast
poll方法
1 | /** |
同理 pollFirst 和 pollLast
push方法
1 | /** |
pop方法
1 | /** |
offer方法
实际上 offer 是调用的 add 方法,但是区别就在 linkedlist 继承了 Dequ 和 List 父类。一般当 queue 用的时候要用 offer/push/pop 而当使用 list 的时候用 add/remove 。
总结
通过查看LinkedList的源码可以发现:
- 首先可以确定LinkedLIst是一个通过Node结构实现的双向链表
- 其次通过add和remove方法可以看出它不向ArrayList一样,需要对容量进行扩容操作,而是通过‘指针’指向前后节点实现的‘连接’。
- 然后通过get方法可以看出查找一个特定位置上的非常麻烦,需要遍历List,尽管使用了二分的方式进行了优化,但是查找性能依旧不能和ArrayList相比。